International Medical Clinic (IMC) specialises in family, paediatric and travel medicine, with the medical needs of the international community of Singapore and South East Asia very much in mind.
With two General Practice Clinics and a specialist Paediatric Clinic, IMC strive to provide a high standard of healthcare in a caring, friendly and familiar environment. Their patient care is enhanced by their staff of selected medical professionals from a diverse range of countries encompassing North America, Europe, Australia and Asia.
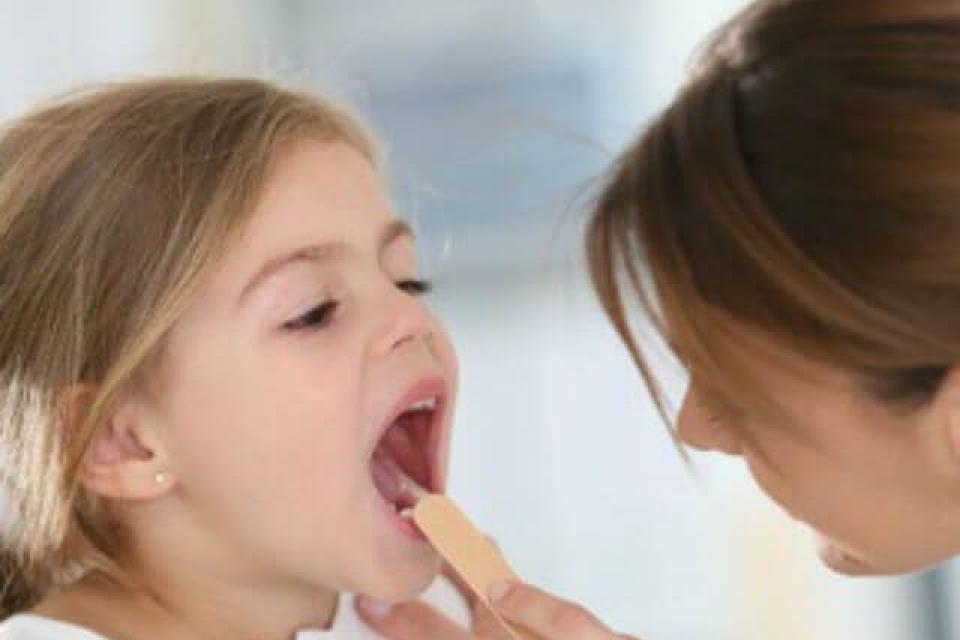
Hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD) occurs mostly in children under five. It is highly infectious and endemic in Singapore, where periodic outbreaks occur in schools and nurseries. It is caused by a family of Enteroviruses and transmitted via infected secretions over shared surfaces.
HFMD is generally mild and self-limiting, with symptoms of fever, blisters on hands, feet and buttock areas and painful oral ulcers. Most cases are managed at home with good hydration and pain relief. A minority (1-2%) may require hospitalisation because of poor feeding. HFMD caused by Enterovirus 71 can be more severe or rarely have complications like brain inflammation. This virus is uncommon but on the rise.
High standards of home/personal hygiene help to reduce infectious risk. Regular hand washing and cleaning shared toys and common play areas should be implemented. Clothes, towels and eating utensils should not be shared.
Children are infectious for up to two weeks until all blisters have dried up. Parents are encouraged to see their doctor early when their child presents with suspicious symptoms. This allows early diagnosis, isolation and identification of severe cases for management.
Advisory to parents: what you should know about…
The following is a set of advice to help you and your family to manage HFMD at home.
1. You should consult a doctor early if your child has fever, mouth ulcers and rashes on the palms, soles or buttocks.
2. Maintain high standards of personal and environmental hygiene to minimise the spread of HFMD. You should ensure that your children adopt the following good practices:
Wash hands with soap before eating and after going to the toilet;
Cover mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing;
Do not share eating utensils.
Do not share any food or drinks.
3. Children with HFMD should remain athome until all the blisters have dried up. They should avoid contact with other children during this period. They should not be brought to any public or crowded places and should stay away from school and child care for this entire period and not return until they have fully recovered.
4. As HFMD is infectious, other children living in the same household may also get infected. Please check these children daily before they are allowed to go to school, child care centre or other pre-school centres. Children who come down with the infection should remain at home.
Please be alert to any change in your child’s normal behaviour, e.g. irritation or sleepiness. If in doubt, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Brought To You By Expat Choice